Heard about the new Snapdragon 660 and 630 processors?
Want to know the different between Snapdragon 660 and Snapdragon 630 processors? Then this is the guide you are looking for.
Let’s start understanding the must know differences between Snapdragon 660 and 630 processors
Snapdragon 660 vs Snapdragon 630 – What actually changed?
Snapdragon 660 and Snapdragon 630 are the updated SoC (System on Chip) for Snapdragon 652 and Snapdragon 625 respectively. Snapdragon 660 and 630 are launched on May 9, 2107 by Qualcomm, exclusively to support mid-range smartphones. We, at Geek Dashboard, will walk you through the detailed comparison: Snapdragon 660 vs Snapdragon 630.
The major differences between Snapdragon 660 and Snapdragon 630 are listed below:
- Processor inside CPU [Central Processing Unit]
- DSP [Digital Signal Processing] Technology and HVX [Hexagon Vector eXtensions] implementation
- Wi-Fi Peak Speed, Channel Utilization, DBS [Dual-Band Simultaneous] and Antenna Sharing
- On-Device and external display support
- GPU [Graphics Processing Unit]
- Security Support
- Memory Speed
Let us peep into each difference and analyze which Qualcomm Snapdragon should fit into your next budget smartphone.

Processor inside CPU
From the time, the ‘Core’ technology was introduced, there has been drastic improvement in the processing speed. CPU cores are nothing but the logical division of CPU into n number of processors which can process n times faster than a single processor.
Generally, the processors or CPU are named with number prefixes like dual-core, quad-core, octa-core, hexacore, and deca-core etc.. A dual core CPU is a single CPU (physically), which is logically capable of working like two independent CPUs. Similarly, quad-core indicates four independent CPUs and so on.
Let’s see what former processors of Snapdragon contain. Snapdragon 652 features octa-core CPU (4x ARM Cortex A72, 4x ARM Cortex A53) with a clock speed of 1.8 GHz whereas Snapdragon 652 features octa-core CPU (8x ARM Cortex A53) with a clock speed of 2.0 GHz.
The latest update to the previous Qualcomm processors 652 and 625 looks more devastating. Snapdragon 660 featured with octa-core Qualcomm Kryo 260 CPU but Snapdragon 630 featured with octa-core ARM Cortex A53.
Qualcomm slowly tending to Kryo CPU leaving behind the third-party ARM Cortex processors, as Kryo was designed by Qualcomm for self-purpose. This significantly improved the performance of Snapdragon processor and results will speak about it. One of the latest Snapdragon processors from 800 series, Snapdragon 835 was featured with 8x Qualcomm Kryo 280 CPU. Qualcomm 660 wins the battle between two different processors.
Verdict – Qualcomm Snapdragon 660. Can’t compromise on the processing power of CPU.
DSP Technologies
Hexagon DSP Processor was developed by Qualcomm to support processing needs of multimedia and modem operations. Hexagon majorly concentrates on Audio, Images and other computations. There is a slight difference in the hexagon processors used in Snapdragon 660 and Snapdragon 630. Snapdragon 660 comes with Qualcomm Hexagon 680 DSP, but the counterpart comes with Qualcomm Hexagon 642 DSP. Snapdragon 835 is the premium tier processor which is featured with Qualcomm Hexagon 682 DSP. Compared to the DSP technologies implemented, Snapdragon 660 definitely outsmarts Snapdragon 630.
HVX (Hexagon Vector eXtensions) is the latest technology (algorithm) developed as an upgrade to the current Hexagon technology used mainly for wide-vector processing. This will definitely improve the performance and reduce the power consumption. Wide-vector processing includes enhancements for Video Processing, Camera Post-Processing, Computer Vision and Camera Streaming.
Results depicts HVX dominance over Hexagon DSP: 3x faster processing and 10x lower energy consumption
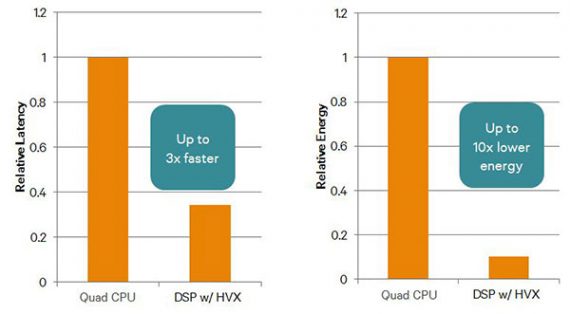
Fortunately, Snapdragon 660 falls under the category which uses HVX which is lacking feature in Snapdragon 630.
Verdict – Qualcomm Snapdragon 660. HVX seems must and should
Wi-Fi Technology Discrepancies
Peak Speed, Channel Utilization, MIMO Configuration, DBS (Dual-Band Simultaneous), LTE/Wi-Fi Antenna sharing are the major setbacks for Snapdragon 630 compared to Snapdragon 660.
Peak speed is the data transferring capacity of a processor over a medium like Wi-Fi. Peak speed is measured in Mbps (Megabits per second). Snapdragon 660 exhibited 867 Mbps peak speed and Snapdragon exhibited 433 Mbps peak speed when tested.
Snapdragon 630 is unable to use 160 MHz channel for data transmission across Wi-Fi. It is restricted to use only 20 MHz, 40 MHz, and 80 MHz channels. Snapdragon 660 has given supreme privilege to use 160 MHz channel for effective utilization.
MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) is a wireless communication technology which is used to transmit data from source to destination. The MIMO configuration is measured using streams. 1-stream implies 1 transmit and 1 receive radio chains. Similarly, 2-stream implies 2 transmit and 2 receive radio chains which can transmit a given data more effectively. Snapdragon 660 possess 2-stream MIMO configuration whereas Snapdragon 630 stuck with 1-stream MIMO.
DBS [Dual-Band Simultaneous] is the technology in which both the bands of the Wi-Fi routers i.e. 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz are simultaneously utilized for data transmission. Snapdragon 660 beats 630, as 630 lacks this feature. Sharing of LTE network over Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity has been a unique feature to Snapdragon 660 which is missing in Snapdragon 630.
Verdict – Qualcomm Snapdragon 660. All these features together certainly makes the difference
On-Device and External Display Support
The significant variation between Snapdragon 660 and 630 was shown in the display. On-Device display support includes compatible screen size, resolution and mode of display.
Snapdragon 660 can extend its support to the screen size of 2560 X 1600. Unfortunately, Snapdragon 630 can’t extend its support beyond 1920 X 1200 screen size. This compatibility issue limits Snapdragon 630 to HD (1080p) display, but the latter can display quad HD (4x720p). Snapdragon 660 supports WQXGA but Snapdragon 630 can only support QXGA.
QXGA (Quad Extended Graphics Array) is a display resolution of 2048 X 1536 with 4:3 aspect ratio
WQXGA (Wide Quad Extended Graphics Array) is a display resolution of 2560 X 1600 with 16:10 aspect ratio
Snapdragon 660 can support maximum external display up to 4K, but Snapdragon 630 can support maximum external display up to 1080p.
Verdict – Neutral. Since mid-range budget smartphones can’t zoom into this feature that much
GPU
GPU is the Graphical Processing Unit, often called as Visual Processing Unit is an electronic device to power up visual graphics and image processing. The usage of GPU ranges from embedded systems to massive gaming consoles and Smartphones find its way in between them.
Qualcomm relies mostly on Adreno GPUs designed by them. This paves a way to introduce Qualcomm Adreno 512 GPU in Snapdragon 660 and Qualcomm Adreno 508 GPU in Snapdragon 630. This seems a setback for 630 but still can light up the mid-range smartphones for sure.
Verdict – Neutral. Since implementation is not on high-end will certainly suffice mid-rangers
Security Support
Both the Snapdragon processors can provide stunning mobile security with a smart camera, App protection with Qualcomm Processor Security. But Snapdragon 660 had an added advantage of hardware token. Hardware token is the one hardware compatibility which can read biometrics like thumb impression for unlocking the screen, digital payments etc wherever you need a password. Snapdragon 660 held an upper hand in providing security support.
Verdict – Qualcomm Snapdragon 660. Hardware token is critical
Memory Speeds
Memory speed is nothing but the rating given to the RAM. This was first tested and rated by chip manufacturer in time (measured in nanoseconds) and then by module producer in terms of frequency (measured in MHz). In fact, the inverse of what chip manufacturer measured will be the result of what module producer publishes.
Qualcomm Snapdragon 660 rated at 1866 MHz in Memory speed while the competitor Snapdragon 630 rated at just 1333 MHz, seems fancy but not comparable to 660. Snapdragon 660 wins in memory speed too.
Verdict – Qualcomm Snapdragon 660. Memory speed matters
Bonus: We have already covered the difference of Snapdragon 821 and 820. You can find it here.
Final Verdict about Snapdragon 660 vs 630
After the detailed analysis of Snapdragon 660 vs Snapdragon 630, one can surely go with Snapdragon 630 if they are least bothered about the security, memory speeds, and next-gen Wi-Fi technologies and power packed processor. As a smartphone user, we don’t want to compromise on any of the above and hence our recommendation was Snapdragon 660 without any second thought.
